Cardiovascular System
The cardiovascular system comprises the heart and a vast network of blood vessels that work together to circulate blood throughout the body. It supplies oxygen and essential nutrients to tissues, removes waste products, and plays a vital role in maintaining homeostasis, regulating body temperature, and supporting immune and hormonal functions.
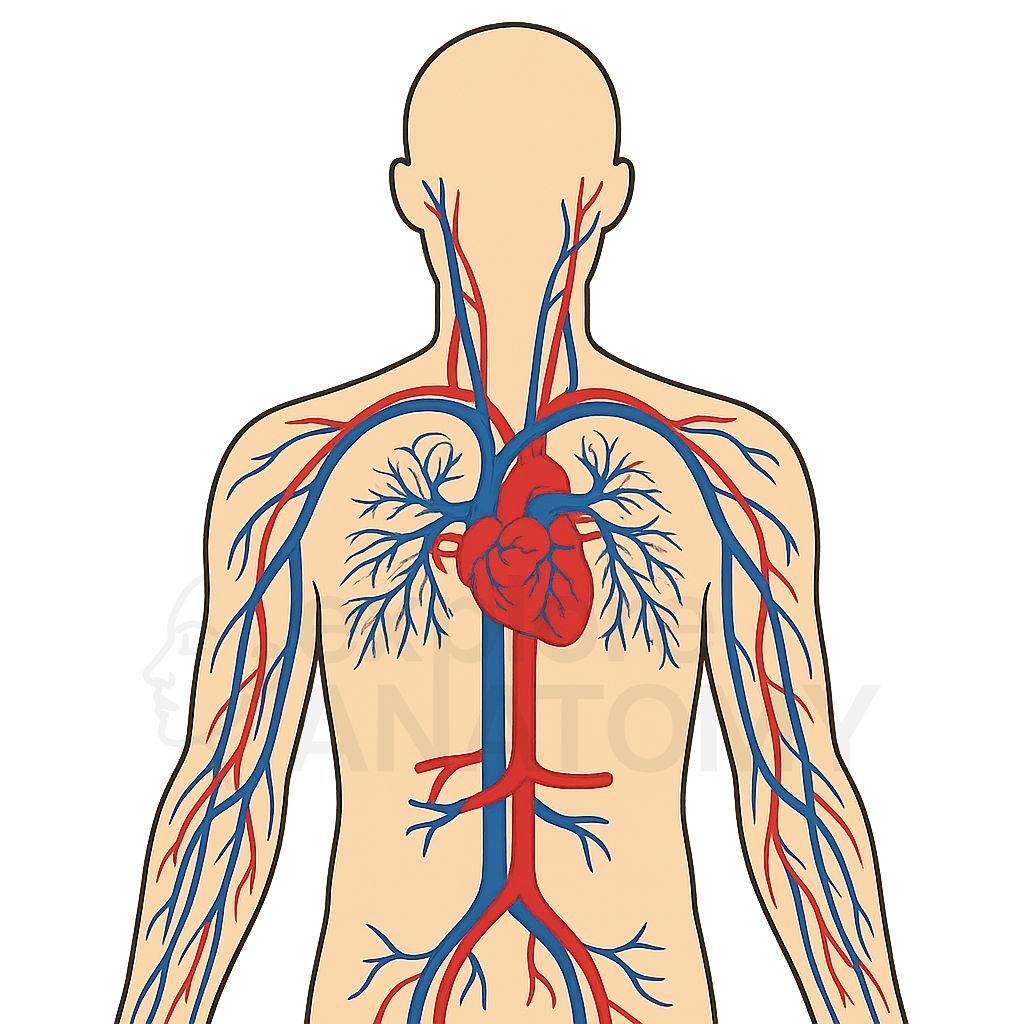
Search Cardiovascular System
Discover the various components and structures that make up the Cardiovascular System.
Cardiovascular System Components
Abdominal Aorta
Part of descending aorta within the abdomen.
Anterior Cardiac Veins
Drain directly into the right atrium.
Anterior Interventricular Branch
Supplies anterior interventricular septum (LAD).
Anterior Tibial Arteries
Supply anterior compartment of the leg.
Aortic Arch
Curved portion of the aorta giving rise to major arteries.
Aortic Valve
Valve between left ventricle and aorta.
Ascending Aorta
Initial portion of the aorta emerging from the heart.
Auricles
Small muscular pouches of each atrium.
Axillary Arteries
Continuation of subclavian arteries into the armpit.
Axillary Veins
Drain the upper limbs and join with subclavian veins.
Basilic Veins
Superficial veins of the medial upper limb.
Brachial Arteries
Major artery of the upper arm.
Brachiocephalic Artery
The brachiocephalic artery is the first major branch of the aortic arch, supplying oxygenated blood to the right side of the head, neck, and upper limb through the right common carotid and subclavian arteries.
Brachiocephalic Trunk
First major branch off the aortic arch.
Brachiocephalic Veins
Formed by the union of subclavian and internal jugular veins.
Cephalic Veins
Superficial veins of the lateral upper limb.
Chordae Tendineae
Tendon-like cords attaching valve leaflets to papillary muscles.
Circumflex Branch
Curves around to the posterior heart.
Common Carotid Arteries
Major arteries supplying blood to the head and neck.
Common Iliac Arteries
Branch from abdominal aorta to supply the lower limbs.
Common Iliac Veins
Drain blood from the pelvis and lower limbs.
Coronary Sinus
Collects blood from coronary veins.
Crista Terminalis
Smooth muscular ridge in the right atrium.
Descending Aorta
Portion of the aorta descending through thorax and abdomen.
Dorsalis Pedis Arteries
Supply blood to the dorsal surface of the foot.
Dorsal Venous Arch
Superficial venous network on the dorsum of the foot.
External Carotid Artery
Supplies blood to the face and scalp.
External Iliac Arteries
Continue into the legs as femoral arteries.
External Iliac Veins
Drain lower limbs and join internal iliac veins.
External Jugular Veins
Drain blood from the face and scalp.
Femoral Arteries
Main arteries supplying the thighs.
Femoral Veins
Major deep veins of the thigh.
Fibrous Pericardium
Outer layer of the pericardium made of dense connective tissue.
Fossa Ovalis
Remnant of the fetal foramen ovale.
Great Cardiac Vein
Drains blood from the anterior surface of the heart.
Great Saphenous Vein
Longest vein in the body, running along the leg.
Heart
Muscular organ responsible for pumping blood throughout the body.
Inferior Vena Cava
Returns deoxygenated blood from lower body.
Interatrial Septum
Wall separating the left and right atria.
Internal Carotid Artery
Supplies blood to the brain.
Internal Iliac Arteries
Supply blood to pelvic organs.
Internal Iliac Veins
Drain pelvic organs.
Internal Jugular Veins
Drain blood from the brain and deep structures of the head.
Interventricular Septum
Wall separating the left and right ventricles.
Left Atrium
Receives oxygenated blood from the lungs.
Left Common Carotid Artery
Supplies the head and neck.
Left Coronary Artery
Supplies blood to left side of heart.
Left Inferior Pulmonary Vein
Returns oxygenated blood from left lung.
Left Pulmonary Artery
Carries blood to left lung.
Left Subclavian Artery
Supplies the left upper limb.
Left Superior Pulmonary Vein
Returns oxygenated blood from left lung.
Left Ventricle
Pumps oxygenated blood into systemic circulation.
Marginal Branch
Supplies right ventricle along the margin.
Median Cubital Vein
Connects cephalic and basilic veins at the elbow.
Middle Cardiac Vein
Drains the posterior heart.
Mitral Valve
Valve between the left atrium and left ventricle.
Moderator Band
Muscular band of heart tissue found in the right ventricle.
Papillary Muscles
Muscles that anchor the heart valves via chordae tendineae.
Parietal Layer
Lines the internal surface of the fibrous pericardium.
Pericardial Cavity
Space between parietal and visceral layers of the serous pericardium containing fluid.
Pericardium
Double-walled sac containing the heart and the roots of the great vessels.
Popliteal Arteries
Continuation of femoral arteries behind the knee.
Popliteal Veins
Drain blood from the knee region.
Posterior Interventricular Branch
Supplies posterior interventricular septum.
Posterior Tibial Arteries
Supply posterior compartment of the leg.
Pulmonary Trunk
Carries deoxygenated blood from right ventricle to lungs.
Pulmonary Valve
Valve between right ventricle and pulmonary trunk.
Radial Arteries
Supply the lateral aspect of the forearm and hand.
Right Atrium
Receives deoxygenated blood from the body.
Right Coronary Artery
Supplies blood to right side of heart.
Right Inferior Pulmonary Vein
Returns oxygenated blood from right lung.
Right Pulmonary Artery
Carries blood to right lung.
Right Superior Pulmonary Vein
Returns oxygenated blood from right lung.
Right Ventricle
Pumps blood to the lungs via pulmonary artery.
Serous Pericardium
Inner layer of the pericardium consisting of parietal and visceral layers.
Small Cardiac Vein
Drains right atrium and ventricle.
Small Saphenous Vein
Superficial vein of the posterior leg.
Subclavian Arteries
Supply blood to the arms and part of the brain.
Subclavian Veins
Carry blood from the upper limbs to the heart.
Superior Vena Cava
Returns deoxygenated blood from upper body.
Thoracic Aorta
Part of descending aorta within the chest.
Trabeculae Carneae
Irregular muscular columns on the walls of the ventricles.
Tricuspid Valve
Valve between the right atrium and right ventricle.
Ulnar Arteries
Supply the medial aspect of the forearm and hand.
Visceral Layer (Epicardium)
Covers the external surface of the heart.