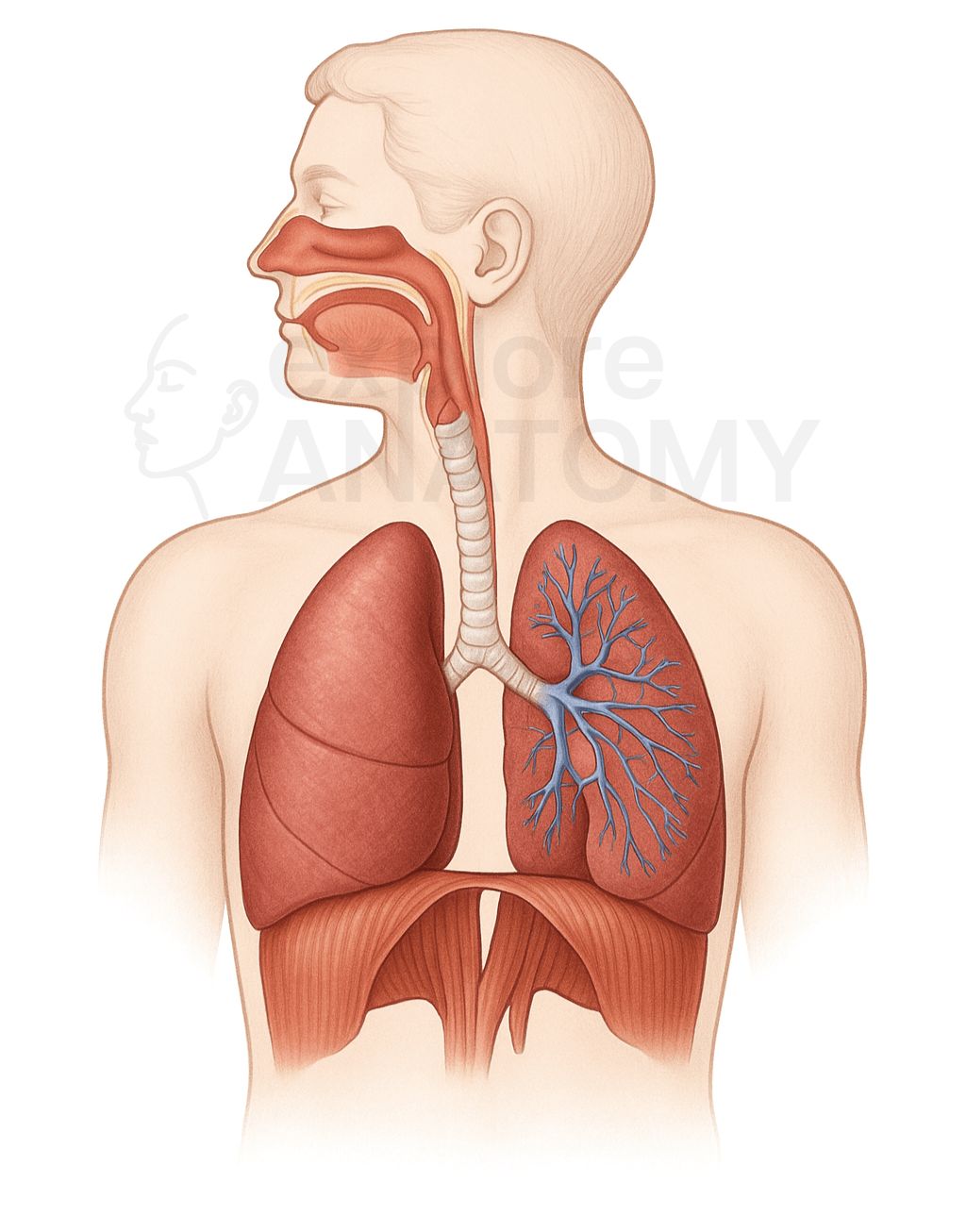
Respiratory System
The respiratory system is responsible for the exchange of gases between the body and the environment. It brings oxygen into the lungs for delivery to the bloodstream and removes carbon dioxide produced by cells, enabling cellular respiration and maintaining acid-base balance in the body.
Search Respiratory System
Discover the various components and structures that make up the Respiratory System.
Respiratory System Components
Alveolar Ducts
Lead to alveolar sacs.
Alveolar Sacs
Clusters of alveoli.
Alveoli
Microscopic air sacs for gas exchange.
Arytenoid Cartilages
Anchor the vocal cords.
Bronchioles
Smaller airways lacking cartilage.
Bronchopulmonary Segments
Functional subdivisions of lung lobes.
Carina
Ridge at bifurcation of trachea.
Cricoid Cartilage
Only complete ring of cartilage in airway.
Diaphragm
Primary muscle of respiration.
Epiglottis
Flap that prevents food entering airway.
Ethmoidal Sinus
Located in the ethmoid bone.
External Nares (Nostrils)
External openings of the nose.
Frontal Sinus
Located in the frontal bone.
Glottis
Opening between vocal cords.
Horizontal Fissure
Separates superior and middle lobes (right lung).
Intercostal Muscles
Assist with chest expansion and contraction.
Laryngopharynx
Leads to larynx and esophagus.
Larynx
Voice box; connects pharynx to trachea.
Lingula
Tongue-like projection of left lung superior lobe.
Lobes of Left Lung
Superior, Inferior.
Lobes of Right Lung
Superior, Middle, Inferior.
Lungs
Main organs of respiration.
Maxillary Sinus
Located in the maxilla.
Meatuses (Superior, Middle, Inferior)
Air passages below each concha.
Nasal Cavity
Warms, moistens, and filters inhaled air.
Nasal Conchae
Increase surface area and turbulence in the nasal cavity.
Nasal Septum
Separates left and right nasal cavities.
Nasopharynx
Posterior to nasal cavity.
Oblique Fissure
Separates lobes in both lungs.
Oropharynx
Posterior to oral cavity.
Paranasal Sinuses
Air-filled spaces in skull bones, connected to nasal cavity.
Parietal Pleura
Lines the thoracic wall.
Pharynx
Muscular tube for air and food passage.
Pleura
Double-layered membrane around lungs.
Pleural Cavity
Space between pleural layers.
Primary Bronchi (Left and Right)
First branches off trachea to lungs.
Pulmonary Capillaries
Surround alveoli for gas exchange.
Respiratory Bronchioles
Start of respiratory zone.
Secondary (Lobar) Bronchi
Branch to each lobe of lung.
Sphenoidal Sinus
Located in the sphenoid bone.
Terminal Bronchioles
Last part of conducting zone.
Tertiary (Segmental) Bronchi
Supply bronchopulmonary segments.
Thyroid Cartilage
Largest cartilage of the larynx.
Trachea
Tube that carries air to bronchi.
Tracheal Cartilages
C-shaped rings supporting the trachea.
Type I Alveolar Cells
Form alveolar wall for gas exchange.
Type II Alveolar Cells
Secrete surfactant to reduce surface tension.
Vestibular Folds (False Vocal Cords)
Protect vocal cords.
Visceral Pleura
Covers lung surface.
Vocal Cords (True Vocal Folds)
Produce sound.