Integumentary System
The integumentary system consists of the skin, hair, nails, and associated glands. It serves as the body's first line of defense, protecting against environmental hazards, regulating temperature, preventing water loss, and enabling sensory perception.
Search Integumentary System
Discover the various components and structures that make up the Integumentary System.
Integumentary System Components
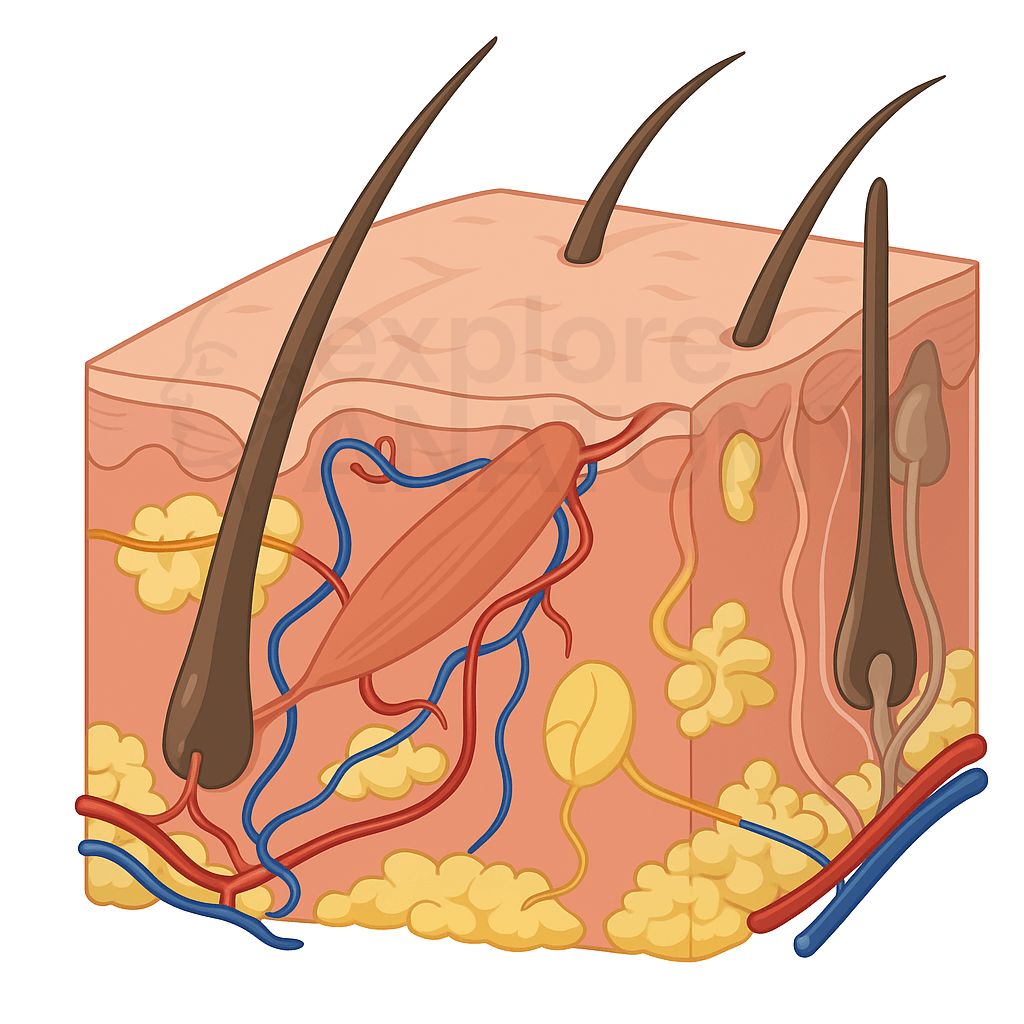
Adipose Tissue
Fat tissue in the hypodermis that insulates and stores energy.
Apocrine Sweat Glands
Sweat glands found in the armpits and genital areas.
Arrector Pili Muscle
Small muscle attached to hair follicles causing hair to stand up.
Carotene
Pigment contributing to the yellow-orange coloration of the skin.
Ceruminous Glands
Specialized sweat glands in the ear canal that produce earwax.
Connective Tissue
Fibrous tissue supporting the skin and other organs.
Cutaneous Blood Vessels
Blood vessels located in the dermis supplying oxygen and nutrients.
Cuticle
Eponychium; tissue at the base of the nail that protects the matrix.
Dermal Papillae
Extensions of the dermis into the epidermis that provide nutrients and sensory functions.
Dermis
Layer below the epidermis providing structure and flexibility.
Eccrine Sweat Glands
Most common sweat glands, found all over the body.
Epidermis
Outer layer of the skin, providing a barrier against environmental factors.
Eumelanin
Type of melanin that produces brown and black pigmentation.
Free Nerve Endings
Pain receptors (nociceptors) and temperature receptors.
Hair
Strands of keratinized cells that grow from follicles beneath the skin.
Hair Bulb
Base of the hair follicle where cells divide and produce the hair shaft.
Hair Follicle
Root of the hair embedded in the skin.
Hair Papilla
Cluster of cells at the base of the hair follicle containing capillaries.
Hair Root
Part of hair within the follicle, undergoing growth.
Hair Shaft
Visible part of hair extending from the follicle.
Hemoglobin
Oxygen-carrying protein in blood responsible for the red coloration of skin.
Hypodermis
Also called subcutaneous layer, consisting of fat and connective tissue.
Lamellated (Pacinian) Corpuscles
Receptors that detect deep pressure and vibration.
Lymphatic Vessels
Vessels responsible for transporting lymph throughout the skin.
Mammary Glands
Glands in females that produce milk during lactation.
Melanin
Pigment responsible for skin color.
Merkel Discs
Receptors that detect light touch and pressure.
Nail Bed
Skin under the nail plate, supplying nutrients.
Nail Matrix
Region of nail growth located beneath the base of the nail.
Nail Plate
Hard, visible part of the nail.
Nails
Hard, keratinized extensions at the tips of fingers and toes.
Papillary Layer
Upper layer of dermis, containing capillaries and sensory neurons.
Pheomelanin
Type of melanin that produces yellow and red pigmentation.
Reticular Layer
Deeper dermal layer, housing collagen and elastin fibers.
Ruffini Endings
Receptors that detect skin stretch and finger position.
Sebaceous Glands
Glands that produce sebum (oil) to lubricate skin and hair.
Sensory Nerve Endings
Nerve endings in the skin that detect sensory information.
Skin
The body's largest organ, which protects internal structures and regulates temperature.
Stratum Basale
Deepest layer of epidermis responsible for cellular regeneration.
Stratum Corneum
Outermost layer of epidermis composed of dead, flattened skin cells.
Stratum Granulosum
Layer of epidermis where keratinization begins.
Stratum Lucidum
Layer found only in thick skin, providing extra protection.
Stratum Spinosum
Layer providing strength and flexibility to skin.
Sweat Glands
Glands that produce sweat to regulate body temperature.
Tactile (Meissner's) Corpuscles
Receptors that detect light touch.