Endocrine System
The endocrine system is composed of glands that secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream to regulate vital body functions. These hormones influence growth, metabolism, reproduction, mood, and homeostasis, ensuring long-term coordination of physiological activities throughout the body.
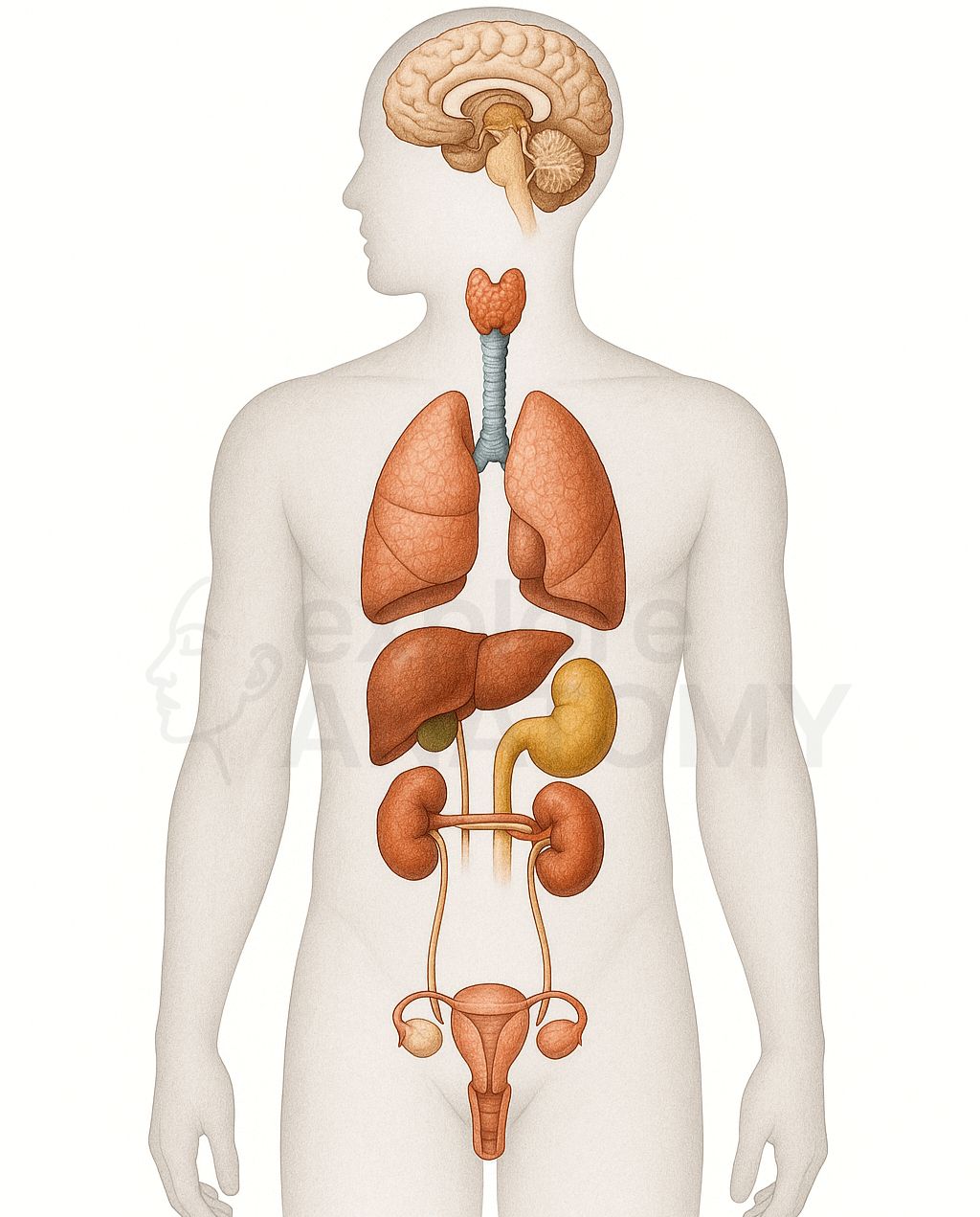
Search Endocrine System
Discover the various components and structures that make up the Endocrine System.
Endocrine System Components
Adrenal Cortex
Produces corticosteroids such as cortisol and aldosterone.
Adrenal Glands
Located above the kidneys, produce hormones for metabolism and stress response.
Adrenal Medulla
Produces adrenaline and norepinephrine in response to stress.
Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH)
Stimulates the adrenal glands to release corticosteroids.
Aldosterone
Regulates sodium and potassium balance in the kidneys.
Androgens
Sex hormones produced in small amounts in both men and women.
Anterior Pituitary (Adenohypophysis)
Produces hormones that regulate other endocrine glands.
Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH)
Regulates water balance by increasing water reabsorption in kidneys.
Calcitonin
Regulates calcium levels in the blood by inhibiting osteoclast activity.
Cortisol
Regulates metabolism, immune response, and stress.
Epinephrine (Adrenaline)
Increases heart rate, blood flow, and metabolism during stress.
Estrogen
Primary female sex hormone responsible for female reproductive development.
Follicle-Stimulating Hormone (FSH)
Stimulates the growth of ovarian follicles and sperm production.
Glucagon
Raises blood sugar by stimulating glucose release from the liver.
Growth Hormone (GH)
Stimulates growth and cell reproduction.
Hypothalamus
Master gland of the endocrine system, regulating the release of hormones from the pituitary.
Inhibin
Inhibits FSH secretion to regulate sperm production.
Insulin
Lowers blood sugar by promoting glucose uptake into cells.
Luteinizing Hormone (LH)
Triggers ovulation and stimulates testosterone production in males.
Melanocyte-Stimulating Hormone (MSH)
Regulates skin pigmentation.
Norepinephrine (Noradrenaline)
Works alongside adrenaline to increase heart rate and blood flow.
Ovaries (Female)
Produce hormones that regulate reproductive function and secondary sexual characteristics.
Oxytocin
Stimulates uterine contractions during childbirth and milk ejection.
Pancreas
Functions as both an endocrine and exocrine gland, regulating blood glucose levels.
Pancreatic Polypeptide
Regulates pancreatic secretion activity.
Parathyroid Glands
Regulate calcium levels by secreting parathyroid hormone.
Parathyroid Hormone (PTH)
Increases blood calcium levels by stimulating calcium release from bones.
Pineal Gland
Produces melatonin to regulate sleep-wake cycles.
Pituitary Gland (Hypophysis)
The master gland controlling other endocrine glands.
Posterior Pituitary (Neurohypophysis)
Stores and releases hormones from the hypothalamus.
Progesterone
Prepares the body for pregnancy and regulates menstrual cycles.
Prolactin (PRL)
Stimulates milk production in females.
Relaxin
Relaxes the uterine muscles and helps prepare the cervix for childbirth.
Somatostatin
Inhibits insulin and glucagon release, balancing blood sugar.
Testes (Male)
Produce hormones that regulate male reproductive function and secondary sexual characteristics.
Testosterone
Primary male sex hormone responsible for male reproductive development.
Thymus
Produces thymosin to regulate the immune system.
Thyroid Gland
Regulates metabolism, growth, and development.
Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH)
Stimulates the thyroid gland to release thyroid hormones.
Thyroxine (T4)
Thyroid hormone that regulates metabolic rate.
Triiodothyronine (T3)
Thyroid hormone that affects energy and metabolism.