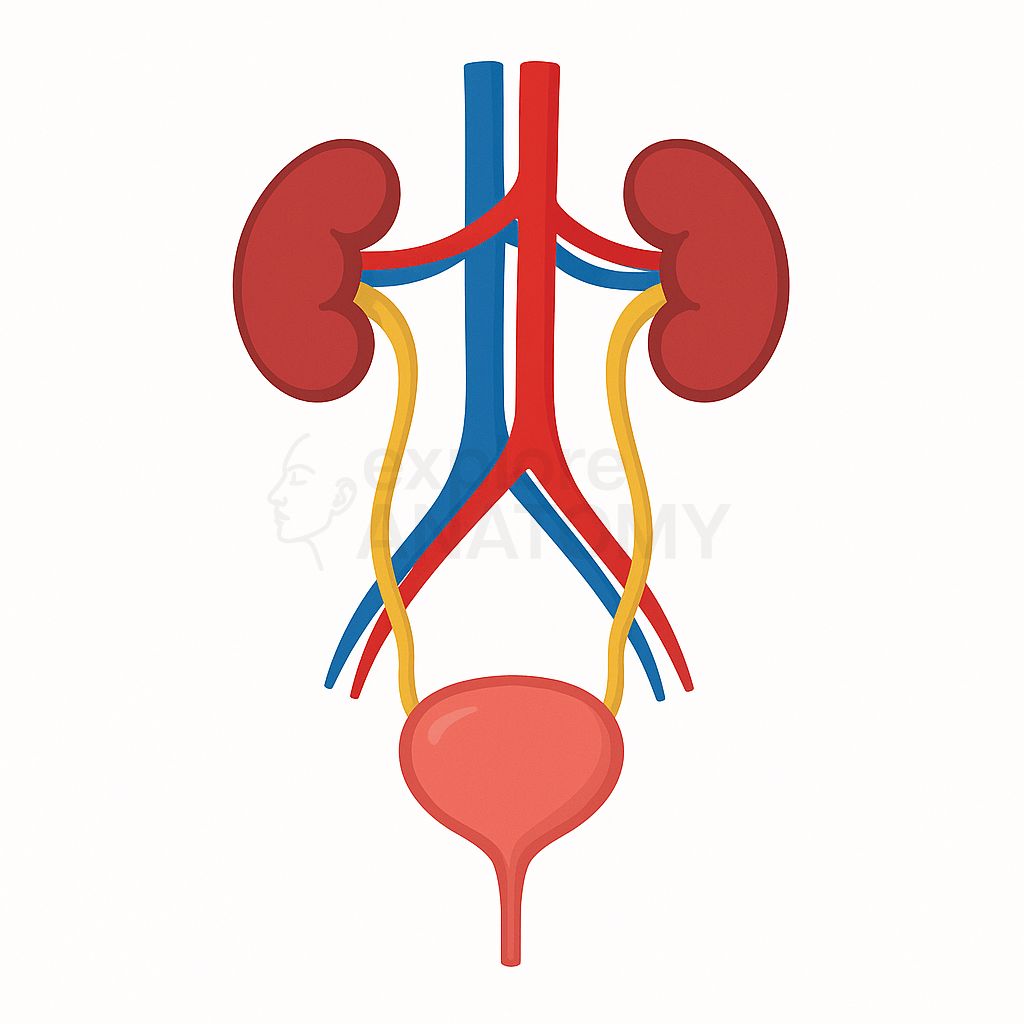
Urinary System
The urinary system filters blood to remove waste products and excess fluids, forming urine that is excreted from the body. It plays a crucial role in maintaining fluid and electrolyte balance, regulating blood pressure, and ensuring the chemical stability of the internal environment.
Search Urinary System
Discover the various components and structures that make up the Urinary System.
Urinary System Components
Afferent Arteriole
Leads into glomerulus.
Arcuate Arteries
Arch over the base of pyramids.
Bladder Neck
Region surrounding internal urethral orifice.
Bladder Peritoneum
Covers superior bladder surface.
Bowman’s Capsule
Surrounds glomerulus; initial urine collection.
Collecting Duct
Final site for water reabsorption.
Detrusor Muscle
Smooth muscle for bladder contraction.
Distal Convoluted Tubule
Regulates electrolytes and pH.
Efferent Arteriole
Drains from glomerulus.
External Urethral Meatus
External urethral opening.
External Urethral Sphincter
Voluntary control of urination.
Female Urethra
Shorter urethra in females.
Glomerulus
Capillary tuft where filtration starts.
Hilum of Kidney
Entry/exit site for vessels, nerves, and ureter.
Interlobar Arteries
Run between renal pyramids.
Interlobular Arteries
Extend into cortex.
Internal Urethral Orifice
Opening from bladder to urethra.
Internal Urethral Sphincter
Involuntary control of urine release.
Kidneys
Primary organs for filtration, fluid balance, and excretion.
Loop of Henle
Creates osmotic gradient in medulla.
Major Calyces
Formed by union of minor calyces.
Median Umbilical Ligament
Remnant of embryonic urachus.
Membranous Urethra
Shortest male urethra segment.
Minor Calyces
Receive urine from renal papillae.
Nephron
Functional unit of kidney.
Papillary Duct
Drains urine into minor calyx.
Pelvic Floor Muscles
Support bladder and urethra.
Pelvic Ureter
Segment within the pelvic cavity.
Perirenal Fat
Cushions and protects kidneys.
Peritubular Capillaries
Surround cortical nephrons.
Prostatic Urethra
Passes through prostate gland.
Proximal Convoluted Tubule
Reabsorbs water, ions, and nutrients.
Renal Artery
Supplies oxygenated blood to kidney.
Renal Capsule
Tough fibrous covering of the kidney.
Renal Columns
Tissue between pyramids extending into medulla.
Renal Cortex
Outer region of the kidney where filtration begins.
Renal Fascia
Connective tissue anchoring kidney.
Renal Medulla
Inner region of kidney containing renal pyramids.
Renal Papilla
Apex of pyramid draining urine into minor calyx.
Renal Pelvis
Funnel-shaped basin collecting urine into ureter.
Renal Pyramids
Cone-shaped tissues in the medulla.
Renal Vein
Drains blood from the kidney.
Segmental Arteries
First branches of renal artery.
Spongy Penile Urethra
Longest male urethra segment.
Trigone
Triangle between ureteral openings and urethra.
Urachus
Fetal remnant connecting bladder to umbilicus.
Ureteral Openings
Where ureters drain into bladder.
Ureteral Orifice
Opening of ureter into bladder.
Ureteropelvic Junction
Where renal pelvis becomes ureter.
Ureterovesical Junction
Ureter entry into bladder.
Ureters
Transport urine to bladder.
Urethra
Carries urine out of the body.
Urinary Bladder
Stores urine until micturition.
Urogenital Diaphragm
Supports pelvic organs, surrounds sphincter.
Vasa Recta
Capillaries around loop of Henle.