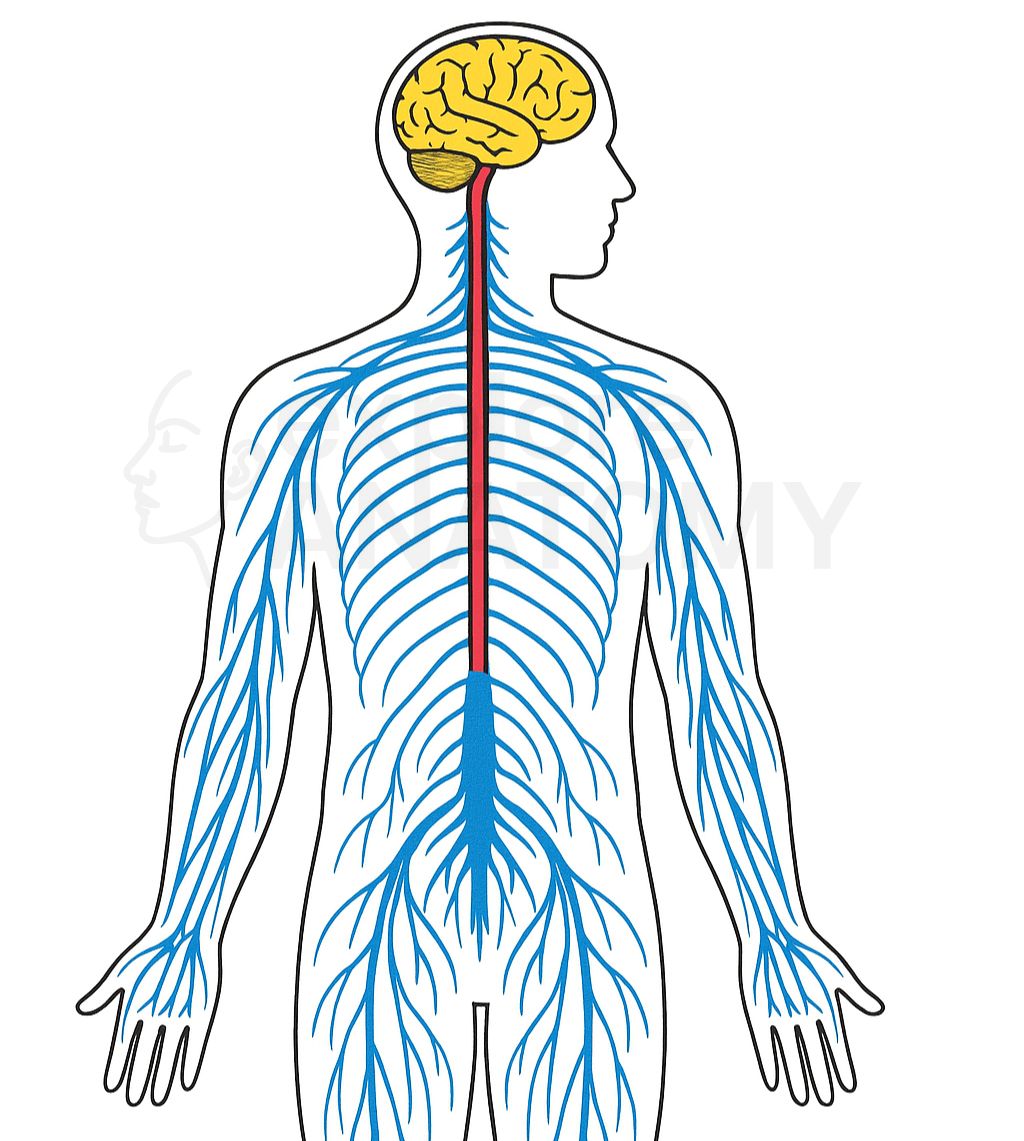
Nervous System
The nervous system is the body’s communication and control center, consisting of the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nerves. It detects and processes sensory information, coordinates voluntary and involuntary actions, and enables functions like thought, emotion, movement, and reflexes.
Search Nervous System
Discover the various components and structures that make up the Nervous System.
Nervous System Components
Abducens Nerve
The abducent nerve (cranial nerve VI) is a motor nerve that controls the lateral rectus muscle of the eye, enabling outward movement (abduction) of the eyeball.
Amygdala
Involved in emotion and memory.
Anterior Cerebral Artery
The anterior cerebral artery (ACA) is a key branch of the internal carotid artery that supplies blood to the medial surfaces of the frontal and parietal lobes, crucial for lower limb motor and sensory control.
Arachnoid Mater
Middle meningeal layer.
Arbor Vitae
White matter of the cerebellum.
Basal Ganglia
Group of nuclei involved in movement regulation.
Basilar Artery
The basilar artery is a midline vessel formed by the union of the vertebral arteries, supplying the brainstem, cerebellum, and posterior cerebrum, essential for balance, coordination, and vital functions.
Bony Labyrinth
The bony labyrinth is a system of cavities within the temporal bone housing the cochlea, vestibule, and semicircular canals, essential for hearing and balance.
Brachial Plexus
Nerve network for the upper limb.
Cauda Equina
Bundle of spinal nerves below the conus medullaris.
Cerebellar Hemispheres
Lateral portions of the cerebellum.
Cerebellar Peduncles
Connect the cerebellum to the brainstem.
Cerebellum
Coordinates movement and balance.
Cerebral Aqueduct
Connects third and fourth ventricles.
Cerebral Cortex
Outer layer of cerebrum responsible for complex thought processes.
Cerebral Peduncles
Connect the cerebrum to the brainstem.
Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF)
Protective fluid in brain and spinal cord.
Cerebrum
Largest part of the brain responsible for voluntary actions, learning, and memory.
Cervical Plexus
Network of nerves supplying neck and shoulder.
Cervical Spinal Cord
Upper part of the spinal cord.
Choroid Plexus
Produces cerebrospinal fluid.
Cingulate Gyrus
Processes emotions and behavior regulation.
Conus Medullaris
Terminal end of the spinal cord.
Corpus Callosum
Connects the left and right cerebral hemispheres.
Cranial Nerves
Twelve pairs of nerves that emerge from the brain.
Diaphragma Sellae
Covers the pituitary gland.
Dorsal Root Ganglion
Contains sensory neuron cell bodies.
Dura Mater
Tough outer meningeal layer.
Epithalamus
Contains the pineal gland, involved in circadian rhythms.
Falx Cerebri
Dural fold between cerebral hemispheres.
Filum Terminale
Fibrous extension from conus to coccyx.
Foramen of Magendie
Median aperture of fourth ventricle.
Foramina of Luschka
Lateral apertures of fourth ventricle.
Fornix
Fiber tract involved in memory.
Fourth Ventricle
Cavity between brainstem and cerebellum.
Frontal Lobe
Controls reasoning, planning, movement, emotions, and problem-solving.
Hippocampus
Essential for memory formation.
Hypothalamus
Regulates autonomic functions, hormones, and homeostasis.
Infundibulum
Connects hypothalamus to pituitary gland.
Insular Cortex
Involved in consciousness, emotion, and homeostasis.
Internal Capsule
White matter structure that carries information to and from the cerebral cortex.
Lateral Ventricles
Paired brain cavities producing CSF.
Lumbar Plexus
Nerve network for abdominal wall and thigh.
Lumbar Spinal Cord
Lower portion of the spinal cord.
Medulla Oblongata
Controls autonomic functions like breathing and heart rate.
Midbrain
Controls visual and auditory systems and body movement.
Occipital Lobe
Responsible for visual processing.
Parietal Lobe
Processes sensory information such as touch, temperature, and pain.
Pia Mater
Innermost layer of meninges.
Pineal Gland
Secretes melatonin to regulate sleep-wake cycles.
Pituitary Gland
Endocrine gland controlling other hormone glands.
Pons
Connects upper and lower parts of the brain.
Sacral Plexus
Nerve network for pelvis and lower limb.
Sacral Spinal Cord
Bottom portion of the spinal cord.
Spinal Cord
Transmits neural signals between brain and body.
Subarachnoid Space
Contains cerebrospinal fluid.
Substantia Nigra
Involved in movement and reward.
Subthalamus
Involved in motor control.
Sympathetic Chain
Series of ganglia for sympathetic nervous system.
Tectum
Dorsal part of midbrain controlling visual and auditory reflexes.
Temporal Lobe
Involved in auditory perception and memory.
Tentorium Cerebelli
Separates cerebellum from cerebrum.
Thalamus
Relay station for sensory and motor signals to the cerebral cortex.
Third Ventricle
Midline cavity of the diencephalon.
Thoracic Spinal Cord
Middle portion of the spinal cord.
Trigeminal Cave
The trigeminal cave, or Meckel’s cave, is a CSF-filled dural pouch in the middle cranial fossa that encloses the trigeminal ganglion, protecting it and enabling sensory transmission from the face.
Vagus Nerve
Major parasympathetic nerve supplying thoracic and abdominal organs.
Ventral Root
Carries motor information from spinal cord.
Vermis
Midline structure of the cerebellum.
Vestibulo-cochlear Nerve
The vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII) is a sensory cranial nerve responsible for hearing and balance, carrying sound and equilibrium information from the inner ear to the brain.